背景
最近有跟同事讨论calico的网络实现的话题,说calico 设计很巧妙,把 2-3层都给处理成了3层,想看看是如何实现的
实现
查看官方文档,发现有几个解释,通过这几个解释我们实际看看Calico中如何实现将2-3层流量都处理成3层的
问题一: 为什么容器中有一条到169.254.1.1的路由规则
1
2
3
4
Why does my container have a route to 169.254.1.1?
In a Calico network, each host acts as a gateway router for the workloads that it hosts. In container deployments, Calico uses 169.254.1.1 as the address for the Calico router. By using a link-local address, Calico saves precious IP addresses and avoids burdening the user with configuring a suitable address.
While the routing table may look a little odd to someone who is used to configuring LAN networking, using explicit routes rather than subnet-local gateways is fairly common in WAN networking.
简单翻译:在Calico网络中,每台主机都充当容器的网关(路由器)。在容器部署中,Calico使用169.254.1.1作为网关路由器的地址。 通过使用link-local地址,Calico节省了宝贵的IP地址,并避免了用户配置合适地址的负担。 虽然对于习惯于配置LAN网络的人来说,路由表可能看起来有点奇怪,但在WAN网络中,使用显式路由而不是子网本地网关是相当常见的。
我们看看容器中的网卡:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
[root@node2 ~]# docker exec -it d3d044626d12 sh
# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: tunl0@NONE: <NOARP> mtu 1480 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ipip 0.0.0.0 brd 0.0.0.0
4: eth0@if55: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1480 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
link/ether d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 0
inet 11.244.104.3/32 brd 11.244.104.3 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
# ip r
default via 169.254.1.1 dev eth0
169.254.1.1 dev eth0 scope link
# exit
[root@node2 ~]# ip a |grep 55
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 655
36 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
inet 179.20.23.41/24 brd 179.20.23.255 scope global noprefixroute ens160
inet 172.17.0.1/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global docker0
55: calic4eb42dc79d@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1480 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
- 容器中有一张eth0网卡,ip是11.244.104.3,对应的另一端veth设备是calic4eb42dc79d
- 容器中只有两条路由规则,分别是默认路由和一条32位路由
- 下一跳是169.254.1.1
从上面容器内的情况可以看到,任何容器流量都是发送给169.254.1.1这个网关的,那么这个网关在哪里,同节点容器如何通信,跨节点容器如何通信呢?我们继续看第二个问题
问题二:为什么我们在host上没有找到ip地址是169.254.1.1的设备?
1
2
3
Why can't I see the 169.254.1.1 address mentioned above on my host?
Calico tries hard to avoid interfering with any other configuration on the host. Rather than adding the gateway address to the host side of each workload interface, Calico sets the proxy_arp flag on the interface. This makes the host behave like a gateway, responding to ARPs for 169.254.1.1 without having to actually allocate the IP address to the interface.
简单翻译是:Calico努力避免干扰主机上的配置。Calico没有将网关地址添加到每个容器网卡的主机端,而是在主机端设备上设置proxy_arp标志。 这使得主机能像网关一样响应169.254.1.1的ARP,而不必实际将IP地址分配给接口。
稍微解释下:
- Calico中容器网卡类型是veth,其中一端在容器内,另一端在主机上
- 这里通过设置主机端设备,开启proxy_arp,同时设置这个设备的mac地址固定为ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee
- 这样任意发送这个设备上的arp请求,该设备都会发送arp reply包,表示自己是网关,可以将后面的包发送给我,我给你们转发
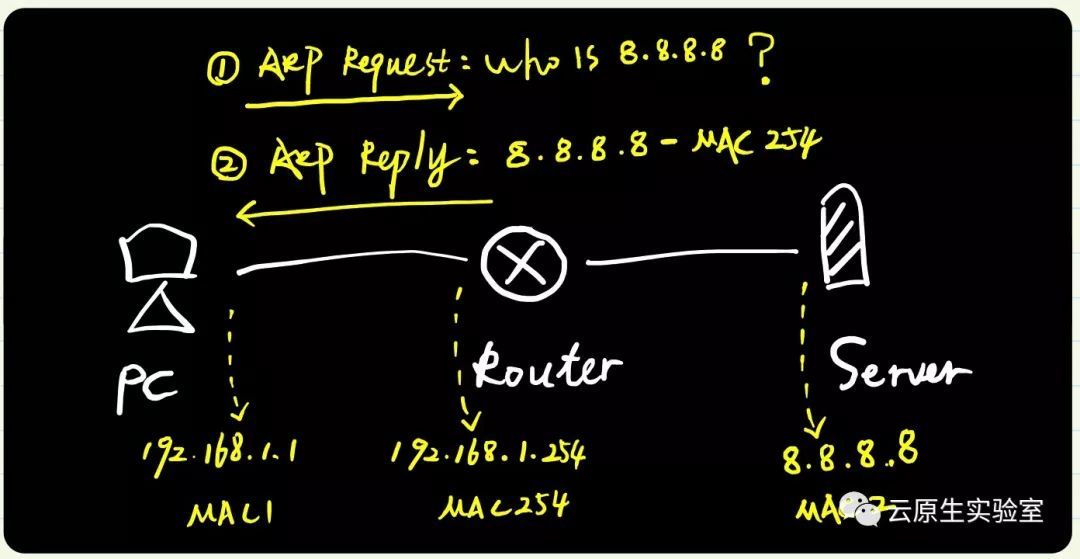
实际在容器中查看:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
[root@node2 ~]# ip link show calic4eb42dc79d
55: calic4eb42dc79d@if4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1480 qdisc noqueue state UP mode DEFAULT group default
link/ether ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff link-netnsid 7
[root@node2 ~]# sysctl -a |grep calic4eb42dc79d |grep proxy_arp
net.ipv4.conf.calic4eb42dc79d.proxy_arp = 1
net.ipv4.conf.calic4eb42dc79d.proxy_arp_pvlan = 0
[root@node2 ~]# ip r |grep calic4eb42dc79d
11.244.104.3 dev calic4eb42dc79d scope link
- calic4eb42dc79d这个设备的mac地址是ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee
- calic4eb42dc79d设备开启了arp代答功能,这样任意发送到这个设备上的arp,且目的mac地址是ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee的请求,都会返回arp reply
这里我们来抓包看看,先看看容器分布:
1
2
3
4
5
6
[root@node1 ~]# kubectl get pods -owide |grep 11.244.104.3
sectest-app-influxdb-deployment-6df667cd75-bmkk5 1/1 Running 4 2d23h 11.244.104.3 node2 <none> <none>
[root@node1 ~]# kubectl get pods -owide |grep 11.244.104.7
sectest-app-rabbitmq-deployment-545f49dd55-bp5tl 1/1 Running 4 2d23h 11.244.104.7 node2 <none> <none>
[root@node1 ~]# kubectl get pods -owide |grep 11.244.135.31
sectest-app-haproxy-deployment-58bfd8b4b-29f79 1/1 Running 2 2d23h 11.244.135.31 node3 <none> <none>
容器同节点通信抓包:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on calic4eb42dc79d, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
14:10:55.717915 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 169.254.1.1 tell 11.244.104.3, length 28
14:10:55.717943 ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee > d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Reply 169.254.1.1 is-at ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, length 28
14:10:56.705970 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.3 > 11.244.104.7: ICMP echo request, id 10, seq 7, length 64
14:10:56.706026 ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee > d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.7 > 11.244.104.3: ICMP echo reply, id 10, seq 7, length 64
14:10:57.705969 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.3 > 11.244.104.7: ICMP echo request, id 10, seq 8, length 64
14:10:57.706019 ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee > d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.7 > 11.244.104.3: ICMP echo reply, id 10, seq 8, length 64
14:10:58.705990 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.3 > 11.244.104.7: ICMP echo request, id 10, seq 9, length 64
容器跨节点通信抓包:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
14:10:08.101925 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Request who-has 169.254.1.1 tell 11.244.104.3, length 28
14:10:08.101948 ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee > d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf, ethertype ARP (0x0806), length 42: Reply 169.254.1.1 is-at ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, length 28
14:10:09.093021 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.3 > 11.244.135.31: ICMP echo request, id 9, seq 7, length 64
14:10:09.093406 ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee > d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.135.31 > 11.244.104.3: ICMP echo reply, id 9, seq 7, length 64
14:10:10.093016 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.3 > 11.244.135.31: ICMP echo request, id 9, seq 8, length 64
14:10:10.093386 ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee > d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.135.31 > 11.244.104.3: ICMP echo reply, id 9, seq 8, length 64
14:10:11.093573 d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf > ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.104.3 > 11.244.135.31: ICMP echo request, id 9, seq 9, length 64
14:10:11.093910 ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee > d6:84:ed:49:d4:cf, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 98: 11.244.135.31 > 11.244.104.3: ICMP echo reply, id 9, seq 9, length 64
在arp请求169.254.1.1后,在主机中的veth设备会返回arp reply包,容器内部会生成一条neigh信息:
1
2
3
[root@node2 ~]# docker exec -it d3d044626d12 sh
# ip neigh
169.254.1.1 dev eth0 lladdr ee:ee:ee:ee:ee:ee STALE
总结
- 从抓包结果看二层通信和三层通信的结果都是类似的,都会先arp请求网关169.254.1.1,再将包转发到网关设备。也就是将二层和三层通信都通过三层进行转发
- 数据包到达主机上的veth设备(容器认为的网关)后,根据主机上的路由进行转发即可
- 主机路由是由bgp(bird)服务维护的
- 由于arp在host的veth就终结了(arp代答的功劳),这种实现有效屏蔽的arp广播,降低广播风暴的威胁